Unveiling the Inner Building Blocks: Exploring the Fundamental Components of the Human Body

The human body, a marvel of engineering, is a complex system composed of countless intricate structures. Delving into the depths of our anatomy and physiology, we embark on a journey of discovery to unravel the fundamental building blocks that make up our physical existence.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16709 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 234 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.85 x 9.69 inches |
The Molecular Foundation
At the most basic level, our bodies are constructed from molecules – the smallest units of matter that sustain life. These molecules fall into four primary categories: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each type plays a distinct role in shaping our body's structure and function.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy to our cells and store it for later use.
- Proteins: Build and repair tissues, facilitate chemical reactions, and regulate bodily functions.
- Lipids: Store energy, form cell membranes, and produce hormones.
- Nucleic Acids: Contain genetic information, controlling cell growth, division, and protein synthesis.
Cells: The Building Blocks of Life
Molecules assemble to form more complex structures known as cells. Cells are the basic unit of life, and the human body comprises an estimated 100 trillion of them. Each cell type has a specialized function, contributing to the overall functioning of our bodies.
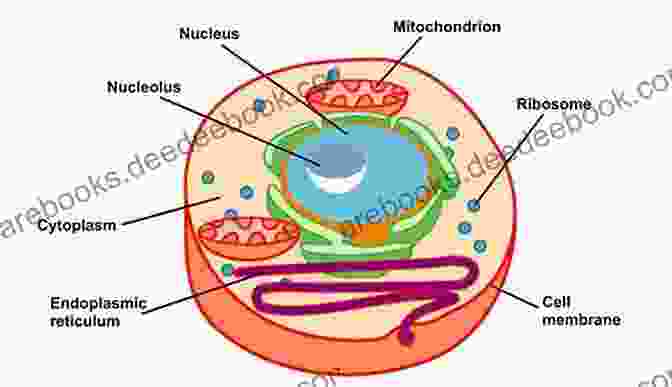
The typical cell consists of:
- Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out.
- Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance that contains organelles.
- Organelles: Specialized structures that perform specific functions, such as protein synthesis, energy production, and waste elimination.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA, the genetic material that guides cell activities.
Tissues: Joining Cells for Collective Function
Cells join together to form tissues, which have a similar structure and function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body:
- Epithelial tissue: Lines the surfaces of organs and cavities, protecting and absorbing.
- Connective tissue: Supports and connects other tissues, providing strength and flexibility.
- Muscle tissue: Enables movement and contracts in response to stimuli.
- Nervous tissue: Transmits electrical signals, allowing communication within the body.
Organs and Organ Systems: Coordinating Functions
Tissues further organize into organs, which perform specific functions. Multiple organs work together within organ systems to carry out complex tasks.
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body (circulatory system).
- Lungs: Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide (respiratory system).
- Brain: Controls thought, emotion, and movement (nervous system).
- Stomach: Digests food (digestive system).
- Skin: Protects the body from external elements (integumentary system).
Homeostasis: Maintaining Internal Balance
The human body operates within a narrow range of conditions to maintain homeostasis – a state of internal equilibrium. Various systems work together to regulate factors such as temperature, pH, and blood sugar levels. This delicate balance ensures optimal functioning and survival.
From the smallest molecules to the complex organ systems, our bodies are a symphony of intricately connected components. Understanding these inner building blocks provides a deeper appreciation for the wonders of biology and the remarkable complexity that defines human existence.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16709 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 234 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.85 x 9.69 inches |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Text
Text Reader
Reader Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Foreword
Foreword Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Dictionary
Dictionary Narrator
Narrator Librarian
Librarian Catalog
Catalog Card Catalog
Card Catalog Borrowing
Borrowing Periodicals
Periodicals Study
Study Research
Research Lending
Lending Academic
Academic Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Special Collections
Special Collections Interlibrary
Interlibrary Study Group
Study Group Thesis
Thesis Storytelling
Storytelling Awards
Awards Reading List
Reading List Book Club
Book Club Theory
Theory Emma Lamb
Emma Lamb T L Christianson
T L Christianson Alan W Wintermute
Alan W Wintermute David Dobbs
David Dobbs J T Ward
J T Ward David Freedberg
David Freedberg Paul Verlaine
Paul Verlaine Andrew Butler
Andrew Butler M E Hubbs
M E Hubbs Diane Allen
Diane Allen Kathleen Valentine
Kathleen Valentine Susan Call Hutchison
Susan Call Hutchison J Griffith Rollefson
J Griffith Rollefson Italo Calvino
Italo Calvino Peter Laufer
Peter Laufer Anthony Esolen
Anthony Esolen Charles Taylor
Charles Taylor Huib Modderkolk
Huib Modderkolk Genevieve Lebaron
Genevieve Lebaron Dymphna Callery
Dymphna Callery
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Austin FordFollow ·5.6k
Austin FordFollow ·5.6k Gregory WoodsFollow ·19.1k
Gregory WoodsFollow ·19.1k Philip BellFollow ·14.4k
Philip BellFollow ·14.4k David MitchellFollow ·16.3k
David MitchellFollow ·16.3k DeShawn PowellFollow ·9.5k
DeShawn PowellFollow ·9.5k Diego BlairFollow ·4.8k
Diego BlairFollow ·4.8k Edwin CoxFollow ·3.1k
Edwin CoxFollow ·3.1k Ethan MitchellFollow ·15.4k
Ethan MitchellFollow ·15.4k

 Gabriel Mistral
Gabriel MistralThe Complete Guide for Startups: How to Get Investors to...
Are you a startup...

 Brian West
Brian WestYour 30 Day Plan To Lose Weight, Boost Brain Health And...
Are you tired of feeling tired, overweight,...

 Allen Ginsberg
Allen GinsbergFox Hunt: (Dyslexie Font) Decodable Chapter (The Kent S...
What is Dyslexia? Dyslexia is a...

 Dwayne Mitchell
Dwayne MitchellElectronic Musician Presents: The Recording Secrets...
By [Author's Name] In the world of music,...

 Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo EmersonA Comprehensive Guide to Deep Learning for Beginners
Deep learning is a subfield...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16709 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 234 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.19 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.85 x 9.69 inches |